Benefits and Limitations of Cloud Computing: A Comprehensive Analysis
Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses and individuals manage data and applications. Offering a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution, it has become a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure. However, despite its many advantages, cloud computing is not without its limitations. This article provides a thorough examination of both the benefits and limitations of cloud computing, helping organizations make informed decisions about adopting this technology.
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (the cloud). It allows users to access and use these services on demand without having to own or maintain physical hardware. Cloud computing is typically categorized into three main service models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers hardware and software tools over the internet, typically used for application development.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, on a subscription basis.
Each of these models offers its own set of benefits and limitations.

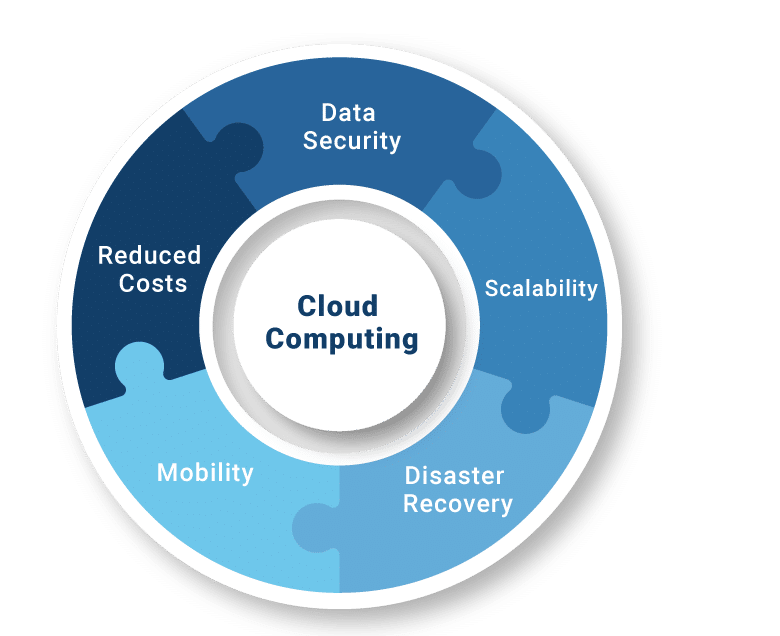
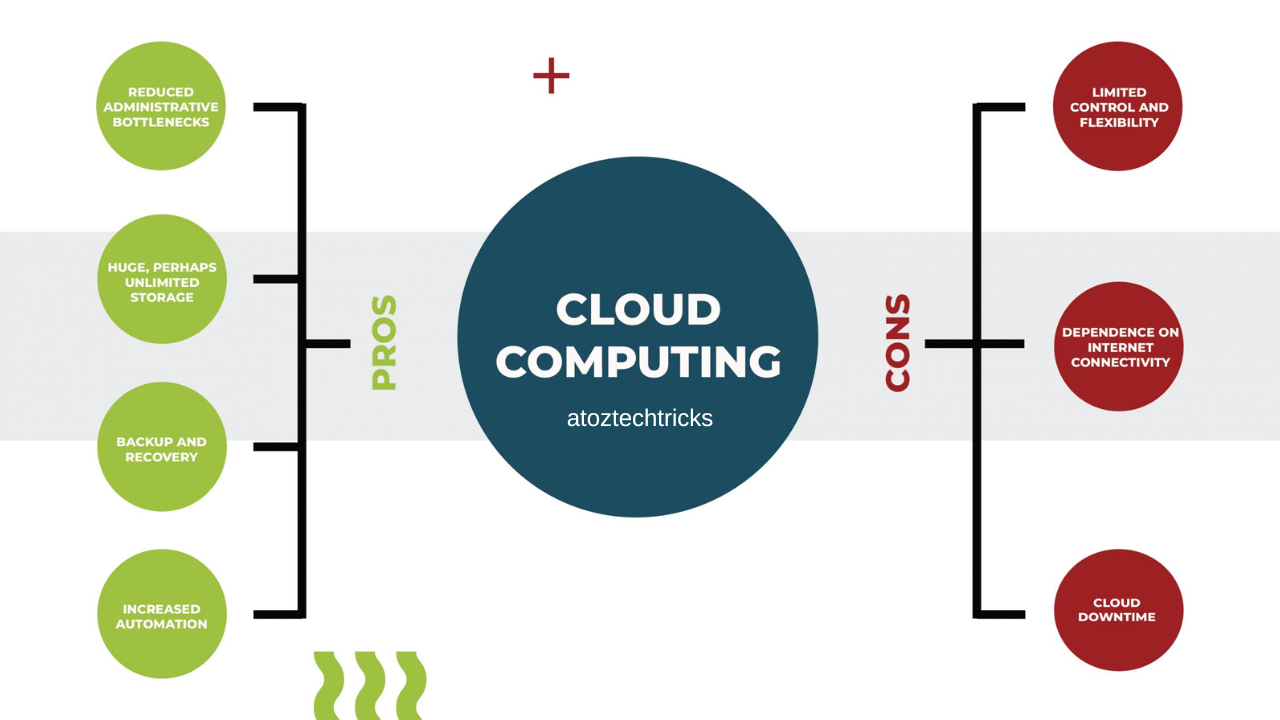
Benefits of Cloud Computing
1. Cost Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its cost-effectiveness. Traditional IT infrastructure requires substantial capital investment in hardware, software, and maintenance. With cloud computing, you pay only for the resources you use. This pay-as-you-go model helps businesses reduce upfront costs and allows for better budget management.
- Reduced Capital Expenditure: No need for large investments in hardware and software.
- Operational Expenses: Costs are shifted to operational expenses, making them more predictable and manageable.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing offers unparalleled scalability and flexibility. Businesses can easily scale their resources up or down based on demand, without the need for significant changes to their existing infrastructure.
- Elasticity: Resources can be scaled up or down in real time based on user needs.
- Global Reach: Access to cloud services from anywhere in the world, providing flexibility for remote work and global operations.
3. Disaster Recovery and Backup
Cloud computing enhances disaster recovery and data backup processes. Cloud providers typically offer robust backup solutions and disaster recovery services that ensure data is protected and can be quickly restored in case of a failure.
- Automated Backups: Regular and automatic backups are part of the cloud service.
- Disaster Recovery: Quick recovery options minimize downtime and data loss.
4. Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud computing facilitates improved collaboration among team members. With cloud-based tools and applications, users can work on documents and projects simultaneously, regardless of their physical location.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Multiple users can edit and share documents in real time.
- Accessibility: Cloud services can be accessed from any device with an internet connection.
5. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Cloud service providers handle the maintenance and updates of software and infrastructure. This means businesses do not need to worry about managing updates, patches, or hardware upgrades.
- Managed Services: Providers take care of software updates, security patches, and hardware maintenance.
- Reduced IT Burden: Frees up internal IT resources to focus on strategic initiatives.

6. Security and Compliance
Leading cloud providers invest heavily in security measures to protect data and comply with industry standards. They offer advanced security features that may be beyond the reach of smaller businesses using on-premises solutions.
- Advanced Security Measures: Includes encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
- Compliance Certifications: Many cloud providers are compliant with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
7. Innovation and Agility
Cloud computing accelerates innovation by providing access to cutting-edge technologies and tools. Businesses can experiment with new technologies and scale their applications rapidly, fostering innovation and agility.
- Access to Latest Technologies: Utilize advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and big data analytics.
- Faster Time to Market: Quickly deploy new applications and services.
Limitations of Cloud Computing
1. Security and Privacy Concerns
Despite advanced security measures, cloud computing introduces certain security and privacy concerns. Data is stored off-site and managed by third parties, which can be a potential risk.
- Data Breaches: Cloud environments can be targets for cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Compliance Risks: Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations can be challenging.
2. Downtime and Service Reliability
Cloud services depend on internet connectivity and the reliability of the cloud provider. Service outages or connectivity issues can disrupt access to critical applications and data.
- Provider Reliability: Service outages or disruptions can impact business operations.
- Internet Dependence: Requires a stable internet connection for access.
3. Limited Control and Flexibility
When using cloud services, businesses may have limited control over the infrastructure and underlying technology. This can affect customization and performance optimization.
- Vendor Lock-In: Moving data and applications between cloud providers can be complex and costly.
- Limited Customization: Restricted ability to customize infrastructure to specific needs.
4. Cost Overruns
While cloud computing can be cost-effective, poor management of resources can lead to unexpected expenses. Without proper monitoring, businesses might end up paying more than anticipated.
- Unexpected Costs: Mismanagement of resources or over-provisioning can lead to higher bills.
- Complex Pricing Models: Understanding and managing various pricing models can be challenging.
5. Compliance and Legal Issues
Data stored in the cloud may be subject to different legal and regulatory requirements depending on the location of the cloud provider and the nature of the data.
- Jurisdictional Issues: Data stored in different countries may be subject to various legal jurisdictions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with industry regulations can be complex.
6. Performance Variability
The performance of cloud services can vary based on several factors, including network conditions, the provider’s infrastructure, and the specific cloud model used.
- Latency Issues: Network latency and performance variability can affect application responsiveness.
- Resource Contention: Shared resources in a cloud environment can lead to performance degradation.
7. Dependency on Cloud Provider
Businesses become dependent on their cloud service providers for service availability, support, and data management. This dependence can pose risks if the provider experiences issues or changes its service terms.
- Service Reliability: Issues with the provider can impact business operations.
- Support Quality: Variability in customer support quality and response times.
Cloud computing offers numerous benefits, including cost efficiency, scalability, enhanced collaboration, and access to advanced technologies. However, it also presents limitations such as security concerns, service reliability issues, and potential cost overruns. Organizations must weigh these benefits and limitations carefully to make informed decisions about cloud adoption.
The Potential of Cloud Computing for Small Businesses and Startups
A strategic approach to cloud computing involves understanding your specific needs, evaluating cloud providers, and implementing robust security and management practices. By doing so, businesses can maximize the advantages of cloud computing while mitigating its potential drawbacks. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest developments in cloud computing will be crucial for leveraging its full potential and maintaining a competitive edge.



Post Comment