Different Types of Exercise and Their Benefits
Exercise is a crucial component of a healthy lifestyle, offering a multitude of physical, mental, and emotional benefits. The various types of exercise serve different purposes and contribute uniquely to overall well-being. This article explores the different types of exercise and their specific benefits, helping you to tailor your workout routine to meet your individual health and fitness goals.
1. Aerobic Exercise
Definition and Examples
Aerobic exercise, also known as cardiovascular or endurance exercise, involves activities that increase your heart rate and improve the efficiency of your cardiovascular system. This type of exercise typically includes activities that can be sustained for extended periods, making it a fundamental part of a well-rounded fitness regimen.
Examples of aerobic exercise include:
- Running: A high-impact activity that boosts cardiovascular fitness and endurance.
- Swimming: A full-body workout that also enhances joint mobility.
- Cycling: An effective lower-body exercise that improves cardiovascular health.
- Walking: A low-impact option suitable for all fitness levels.
- Dancing: An enjoyable way to increase heart rate and coordination.
Benefits
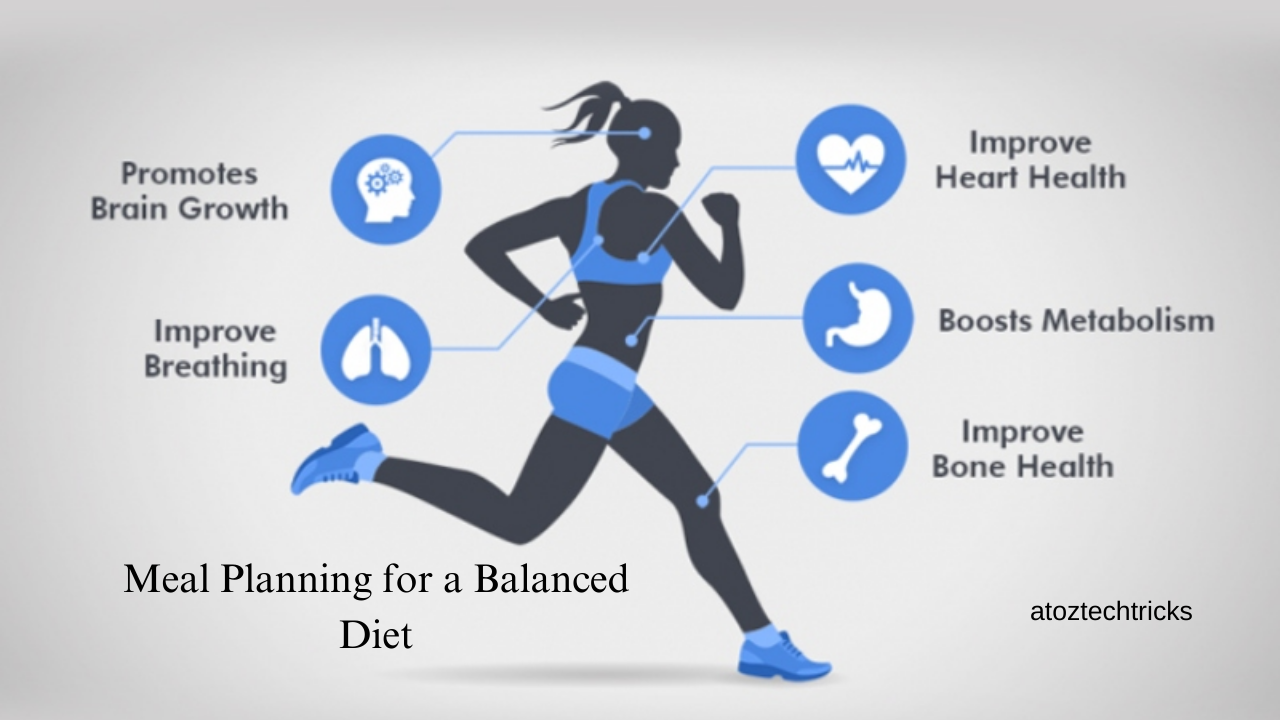
- Cardiovascular Health: Aerobic exercise strengthens the heart, improves blood circulation, and reduces the risk of heart disease.
- Weight Management: Regular aerobic activity helps burn calories and can aid in weight loss or maintenance.
- Endurance and Stamina: Engaging in aerobic exercise enhances overall endurance, making daily activities easier.
- Mood Enhancement: Aerobic exercise releases endorphins, which can improve mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Improved Respiratory Function: It increases lung capacity and efficiency, benefiting overall respiratory health.
2. Strength Training
Definition and Examples
Strength training, also known as resistance training, involves exercises that increase muscle strength and mass through resistance. This type of exercise is essential for building muscle, improving bone density, and enhancing overall body strength.
Examples of strength training exercises include:
- Weight Lifting: Using free weights or machines to target specific muscle groups.
- Bodyweight Exercises: Exercises like push-ups, squats, and lunges that use your body weight as resistance.
- Resistance Band Exercises: Using elastic bands to provide resistance during workouts.
- Kettlebell Training: Incorporating kettlebells to combine strength and cardiovascular benefits.
- Powerlifting: Focusing on heavy lifting with low repetitions to build maximal strength.

Benefits
- Increased Muscle Mass: Strength training helps build and maintain muscle mass, which can enhance metabolism.
- Improved Bone Density: It strengthens bones, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
- Enhanced Functional Strength: Better strength supports daily activities and improves overall physical functionality.
- Boosted Metabolism: More muscle mass increases resting metabolic rate, aiding in weight management.
- Injury Prevention: Strengthening muscles and connective tissues can reduce the risk of injuries.
3. Flexibility Exercises
Definition and Examples
Flexibility exercises focus on improving the range of motion of your muscles and joints. These exercises are important for maintaining overall mobility and preventing stiffness or injury.
Examples of flexibility exercises include:
- Stretching: Static stretches held for some time to increase flexibility.
- Yoga: A practice that combines stretching with breathing and relaxation techniques.
- Pilates: A method that emphasizes core strength, flexibility, and overall body alignment.
- Tai Chi: A low-impact exercise that promotes balance, flexibility, and relaxation through slow, controlled movements.
- Foam Rolling: Using a foam roller to massage and stretch muscles, aiding in recovery and flexibility.
Benefits
- Improved Range of Motion: Enhances the flexibility of muscles and joints, making movements easier and more fluid.
- Reduced Risk of Injury: Greater flexibility can help prevent strains and sprains.
- Enhanced Posture: Flexibility exercises improve alignment and posture, reducing strain on the spine and muscles.
- Stress Relief: Practices like yoga and Tai Chi promote relaxation and stress reduction.
- Better Balance and Coordination: Improved flexibility contributes to better balance and coordination.
Healthy Eating on a Budget: Tips and Strategies for a Nutritious Diet
4. Balance and Stability Exercises
Definition and Examples
Balance and stability exercises are designed to improve core strength, coordination, and overall balance. These exercises are particularly beneficial for enhancing functional fitness and preventing falls, especially in older adults.
Examples of balance and stability exercises include:
- Balance Board Exercises: Using a balance board to improve stability and coordination.
- Single-Leg Stands: Standing on one leg enhances balance and strengthens stabilizing muscles.
- BOSU Ball Workouts: Using a BOSU ball to challenge stability and engage core muscles.
- Stability Ball Exercises: Performing exercises on a stability ball to improve core strength and balance.
- Planks and Variations: Core exercises like planks that engage multiple muscle groups for overall stability.
Benefits
- Enhanced Core Strength: Improves strength and stability of the core muscles, supporting better overall posture and balance.
- Reduced Fall Risk: Improved balance and coordination can help prevent falls, particularly in older adults.
- Better Athletic Performance: Balance and stability are crucial for athletic performance, improving agility and control.
- Injury Prevention: Strengthening stabilizing muscles reduces the risk of injuries during physical activities.
- Improved Functional Fitness: Better balance and stability contribute to more efficient and effective movement in daily activities.
5. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
Definition and Examples
High-intensity interval Training (HIIT) involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by periods of rest or lower-intensity exercise. This type of workout is designed to maximize calorie burn and improve cardiovascular fitness in a shorter amount of time.
Examples of HIIT workouts include:
- Tabata Training: A specific form of HIIT involving 20 seconds of intense exercise followed by 10 seconds of rest, repeated for several rounds.
- Circuit Training: Performing a series of exercises with minimal rest in between to maintain a high heart rate.
- Sprints: Alternating between periods of sprinting and walking or jogging.
- Burpees: A full-body exercise that combines a squat, push-up, and jump, performed at high intensity.
- Jump Rope Intervals: Alternating between high-speed jumping and slower-paced recovery periods.

Benefits
- Efficient Workouts: HIIT provides a time-efficient way to achieve significant fitness gains.
- Increased Calorie Burn: The intense nature of HIIT boosts calorie burn during and after the workout.
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: HIIT enhances cardiovascular fitness and endurance.
- Muscle Preservation: Unlike steady-state cardio, HIIT can help maintain muscle mass while burning fat.
- Variety and Engagement: The varied nature of HIIT workouts can keep exercise interesting and engaging.
6. Functional Training
Definition and Examples
Functional training focuses on exercises that mimic everyday movements, aiming to improve overall functional fitness and enhance performance in daily activities. These exercises typically engage multiple muscle groups and emphasize coordination and balance.
Examples of functional training exercises include:
- Squats: Mimicking the movement of sitting and standing, which strengthens the lower body.
- Lunges: Similar to walking or climbing stairs, improving lower body strength and stability.
- Kettlebell Swings: A dynamic movement that improves strength, power, and coordination.
- Medicine Ball Throws: Engaging the entire body for strength and explosive power.
- Farmers Walk: Carrying heavy weights while walking to enhance grip strength and core stability.
Benefits
- Improved Daily Functionality: Enhances the ability to perform everyday tasks with greater ease and efficiency.
- Enhanced Coordination and Balance: Functional exercises improve overall coordination and balance.
- Reduced Risk of Injury: Strengthens muscles and joints used in daily activities, reducing the risk of injury.
- Increased Core Strength: Many functional exercises engage the core, improving overall stability.
- Better Athletic Performance: Functional training can improve performance in sports and physical activities.
7. Flexibility and Mobility Work
Definition and Examples
Flexibility and mobility work focuses on improving the range of motion of muscles and joints. While flexibility is about lengthening muscles, mobility involves the ability of joints to move freely through their full range of motion.
Examples of flexibility and mobility work include:
- Dynamic Stretching: Stretching exercises are performed in a controlled, smooth manner to prepare the body for activity.
- Foam Rolling: Self-myofascial release to improve muscle flexibility and reduce soreness.
- Joint Mobility Exercises: Targeted movements to enhance the range of motion of specific joints.
- Yoga: Combines stretching with breath control and balance, promoting both flexibility and mobility.
- Active Isolated Stretching: Stretching technique that involves holding each stretch for only a few seconds to increase flexibility.
Benefits
- Enhanced Range of Motion: Improves flexibility and mobility, leading to better movement efficiency.
- Reduced Muscle Tension: Helps release tight muscles and alleviate soreness.
- Improved Joint Health: Enhances joint function and reduces the risk of stiffness or injury.
- Better Athletic Performance: Increased flexibility and mobility contribute to better overall performance in sports and activities.
- Injury Prevention: Regular flexibility and mobility work can reduce the risk of injuries by improving muscle and joint function.
Incorporating a variety of exercise types into your routine can offer a comprehensive approach to fitness, addressing different aspects of health and well-being. Aerobic exercise boosts cardiovascular health, strength training builds muscle and bone density, flexibility exercises enhance range of motion, balance and stability work improve coordination, HIIT provides efficient and intense workouts, functional training supports daily activities, and flexibility and mobility work enhances overall movement quality.

By understanding the benefits of each exercise type, you can create a well-rounded fitness program that meets your individual goals and promotes long-term health. Whether you’re looking to improve endurance, build strength, enhance flexibility, or simply stay active, integrating different types of exercise can lead to a healthier, more balanced lifestyle.



Post Comment